W | X | Y | Z
W
walling-off 
the separation of diseased from healthy tissues by barrier tissues produced by a diseased plant
water-soaked 
a disease symptom in which plant tissues or lesions appear wet, dark, and usually sunken and translucent
water sprout
a small, rapidly growing shoot or branch on a large stem, developed from adventitious tissues
white rot (of wood) 
a type of wood decay resulting from enzymatic action of fungi; it degrades all components of wood, including lignin, leaving the wood light-colored and spongy (contrasts with brown rot)
white rust 
a common name usually used for diseases caused by a member of the Oomycota (the oomycetes) in the genus Albugo
whorl 
the circular arrangement of like parts
wild type
the phenotype characteristic of the majority of individuals of a species under natural conditions
wilt 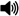

the drooping of leaves and stems from lack of water (i.e., inadequate water supply or excessive transpiration); a vascular disease that interrupts normal water uptake
wind break
a row or other grouping of trees or shrubs used to provide protection against the effects of high-velocity winds
winterburn 
the foliar necrosis, often marginal, of plants that retain their leaves in winter, caused by water deficiency because plants cannot take up water from frozen soils
witches' broom 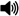

a disease symptom characterized by an abnormal, massed, brushlike development of many weak shoots arising at or close to the same point
wood 
the secondary xylem produced by the vascular cambium in stems and branches of woody plants
wound 
an injury to plant tissues that often breaches barriers (i.e., cuticle, bark, cell walls) that might otherwise exclude pathogens; some pathogens (e.g., viruses) can enter plants only through a wound; a wound may occur from natural growth processes, physical and chemical agents, animals (especially insects), and many human agricultural activities (e.g., pruning)
X
xylem 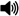

the water- and mineral-conducting, food-storing, supporting tissue of a plant
XLB (acronym for xylem-limited fastidious bacteria) 
the bacterial pathogens of plants found only in the xylem, causing wilt, scorch, and stunting symptoms; vectored by insects that feed on xylem fluid; not sap transmissible; require complex culture media
xylem-limited fastidious bacteria (acronym XLB) 
the bacterial pathogens of plants found only in the xylem, causing wilt, scorch, and stunting symptoms; vectored by insects that feed on xylem fluid; not sap transmissible; require complex culture media
Y
yeast
a unicellular ascomycetous fungus that reproduces asexually by budding
yellows 
a disease characterized by chlorosis and stunting of the host plant
yield
an aggregate of the products resulting from growth or cultivation
Z
zonate 
pertaining to a targetlike development of a tree canker, characterized by successive, perennial rings of callus; referring to any symptom appearing in concentric rings
zoosporangium 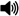 (pl. zoosporangia)
(pl. zoosporangia) 

a sporangium, or spore case, that bears zoospores
zoospore 
a spore of a fungus or funguslike organism with flagella, capable of locomotion in water
zygomycete
an informal term for a member of the Zygomycota
Zygomycota
a fungus group characterized by nonseptate hyphae, sexual spores, and sporangiospores produced in a sporangium; common postharvest pathogens; zygomycetes
zygospore 
a sexual resting spore formed from the union of gametangia in the Zygomycota (the zygomycetes)
